On-device IoT Certificate Revocation Checking with Small Memory and Low Latency
June 2019 – March 2020, supervised by Professor Qian, Chen
Allowing a device to verify the digital certificate of another device is an essential requirement and key building block of many security protocols for emerging and future IoT systems that involve device-to-device communication. However, on-device certificate verification is challenging for current devices, mainly because the
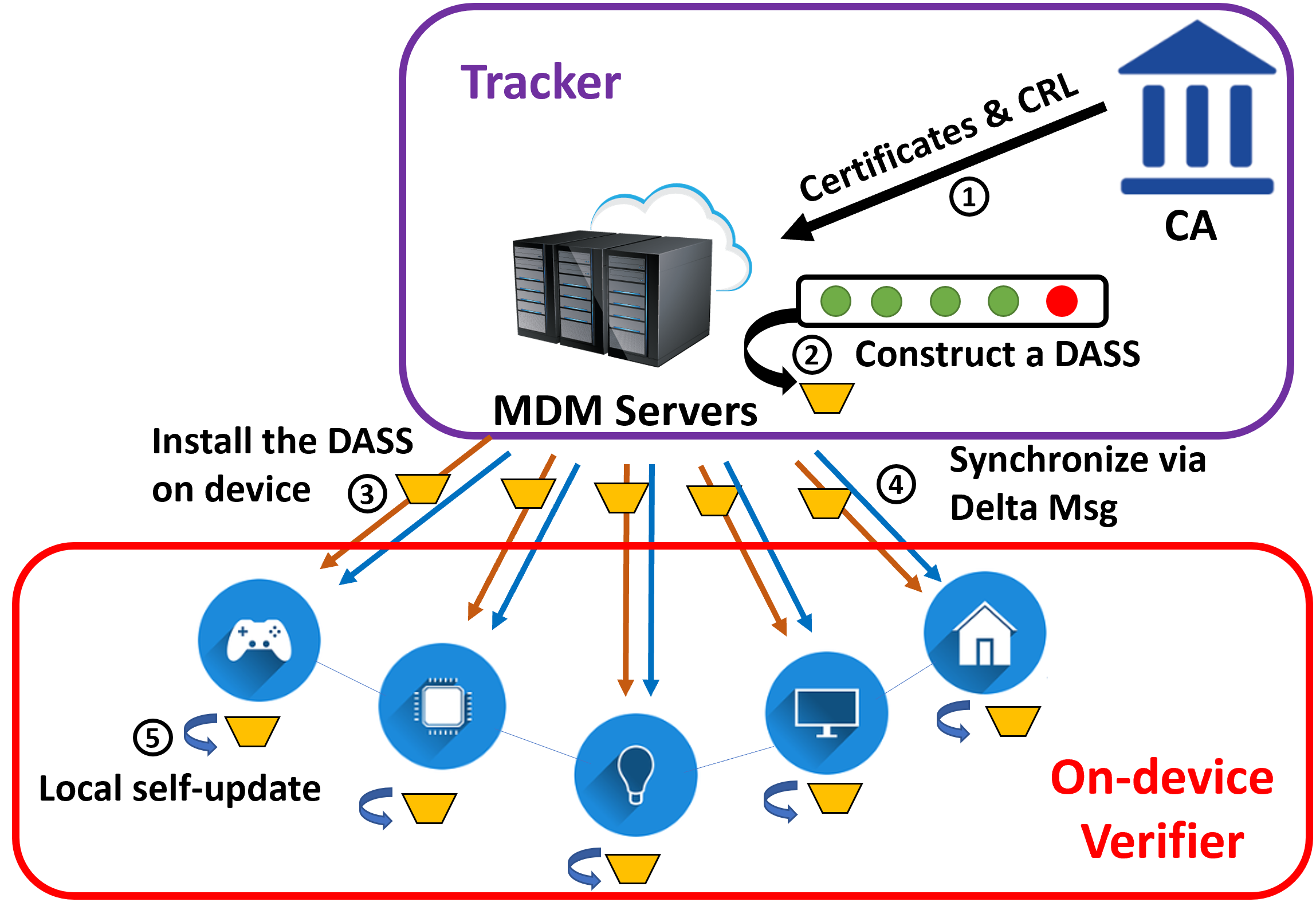
certificate revocation (CR) checking step costs too much resource IoT devices and the synchronization of CR status to devices yields a long latency. This paper presents an on-device CR checking system called TinyCR, which achieves 100% accuracy, memory and computation efficiency, low synchronization latency, and low network bandwidth, while being compatible with the current certificate standard. We design a new compact and dynamic data structure
called DASS to store and query global CR status on a device in TinyCR. Our implementation shows that TinyCR only costs each device 1.7 MB of memory to track 100 million IoT certificates with 1% revocation rate. Checking the CR status of one certificate spends less than 1 microsecond on a Raspberry Pi 3. TinyCR can also be updated instantly when there are new certificates added or revoked.