Overview on Python Programming¶
In this section we are going to have a brief overview on Python programming, basically showing some of the basic Python commands and their short examples. We are going to study more details on them later in the chapter.
Interactive Python¶
In what follows we’ll display the >>> prompt of the
standard Python shell. To enter into an interactive mode, you type in
on your terminal:
$ python
>>>
If you want to exit an interactive mode, you type in:
>>> exit()
$
As already mentioned, multi-line Python statements are best written in a text file (script mode) rather than typing them at the prompt (interactive mode), but some of the short examples below are done at the prompt. When typing a line, if Python recognizes it as an unfinished block, it will give a line starting with three dots, like:
>>> if 1>2:
... print "oops!"
... else:
... print "this is what we expect"
...
this is what we expect
>>>
Once done with the full command, press <return> alone at the ... prompt
tells Python we are done and it executes the command. Note here that
you need to give indentations for the print statements, otherwise you
will see an error message like:
IndentationError: expected an indented block
Now let’s talk about more why this happens.
Indentation: In Python indentation is everything!¶
Most computer languages have some form of begin-end structure, or opening and closing braces, or some such thing to clearly delinieate what piece of code is in a loop, or in different parts of an if-then-else structure like what’s shown above. Good programmers generally also indent their code so it is easier for a reader to see what is inside a loop, particularly if there are multiple nested loops. But in most languages, including Fortran, indentation is just a matter of style and the begin-end structure of the language determines how it is actually interpreted by the computer:
In Python, indentation is everything. There are no begin-end’s, only
indentation. Everything that is supposed to be at one level of a loop must
be indented to that level. Once the loop is done the indentation must go
back out to the previous level. There are some other rules you need to
learn, such as that the “else” in and if-else block like the above has to be
indented exactly the same as as the if. The same is true when
defining a function, in which the lines of actual implementation of a function
should be indented (usually a tab key works) properly to represent
the lines belong to the function.
Before proceeding further, let’s have a quick look at a Python example
of solving the 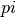 approximation problem in homework 2.
Since we already have implemented the routine in Fortran, we can
easily compare and see how a Python version may look like:
approximation problem in homework 2.
Since we already have implemented the routine in Fortran, we can
easily compare and see how a Python version may look like:
The result should look like:
$ python hw2.py
pi estimator using threshold = 1e-16
1 3.13333333333 0.00825932025646
2 3.14142246642 0.000170187167327
3 3.14158739035 5.26324321148e-06
4 3.14159245757 1.96022357457e-07
5 3.14159264546 8.1294566634e-09
6 3.14159265323 3.61705332352e-10
7 3.14159265357 1.69122493787e-11
8 3.14159265359 8.20232770593e-13
9 3.14159265359 4.08562073062e-14
10 3.14159265359 1.7763568394e-15
11 3.14159265359 0.0
How many spaces to indent each level is a matter of style, but you must be consistent within a single code. The standard is often 4 spaces (which is equivalent to a tab key space).
You can also call the function estimate_pi in the above Python
routine from other Python codes as well. For instance, if you have
a routine called call_estimate_pi_from_hw2.py which looks like:
you can get the same result by running it in the script mode:
$ python call_estimate_pi_from_hw2.py
hw2
pi estimator using threshold = 1e-16
1 3.13333333333 0.00825932025646
2 3.14142246642 0.000170187167327
3 3.14158739035 5.26324321148e-06
4 3.14159245757 1.96022357457e-07
5 3.14159264546 8.1294566634e-09
6 3.14159265323 3.61705332352e-10
7 3.14159265357 1.69122493787e-11
8 3.14159265359 8.20232770593e-13
9 3.14159265359 4.08562073062e-14
10 3.14159265359 1.7763568394e-15
11 3.14159265359 0.0
Notice that in the first line of the output it says hw2,
rather than __main__. The __name__ value
is set to __main__ only if the file is executed as a
script (i.e., $python hw2.py), but not if it is
imported as a module from another routine
as just shown.
We will see more on this in the following sections (Python scripts and modules) and take a look at how to import modules.
Wrapping lines¶
In Python normally each statement is one line, and there is no need to use separators such as the semicolon used in some languages to end a line. On the other hand you can use a semicolon to put several short statements on a single line, such as:
>>> x = 5; print x
5
It is easiest to read codes if you avoid this in most cases.
If a line of code is too long to fit on a single line, you can break it into multiple lines by putting a backslash at the end of a line:
>>> y = 3 + \
... 4
>>> y
7
Comments¶
Anything following a # in a line is ignored as a comment (unless of course the # appears in a string):
>>> s = "This # is part of the string" # this is a comment
>>> s
'This # is part of the string'
There is another form of comment, the docstring, discussed below following an introduction to strings.
Python data types:¶
There are five different standard data types in Python. They can further be grouped into two different object types: mutable and immutable. Mutable objects can be changed after they are created, while immutable objects can’t. We will simply list them here and learn more about them later in this chapter.
- numbers (immutable),
- strings (immutable),
- tuples (immutable),
- lists (mutable),
- dictionaries (mutable).
Strings¶
Strings are specified using either single or double quotes:
>>> s = 'some text'
>>> s = "some text"
are the same. This is useful if you want strings that themselves contain quotes of a different type:
>>> s = ' "some" text '
>>> s = " 'some' text "
You can also use triple double quotes, which have the advantage that such strings can span multiple lines:
>>> s = """Note that a ' doesn't end
... this string and that it spans two lines"""
>>> s
"Note that a ' doesn't end\nthis string and that it spans two lines"
>>> print s
Note that a ' doesn't end
this string and that it spans two lines
When it prints, the carriage return at the end of the line shows up as \n.
This is what is actually stored. When we print s it gets printed as a
carriage return again.
You can put \n in your strings as another way to break lines:
>>> print "This spans \n two lines"
This spans
two lines
We will learn more about strings later, but at this point we can check out built-in String methods.
Docstrings¶
Often the first thing you will see in a Python script or module, or in a function or class defined in a module, is a brief description that is enclosed in triple quotes. Although ordinarily this would just be a string, in this special position it is interpreted by Python as a comment and is not part of the code. It is called the docstring because it is part of the documentation and some Python tools automatically use the docstring in various ways. Also the documentation formatting program Sphinx that is used to create these class notes can automatically take a Python module and create html or latex documentation by using the docstrings, the original purpose for which Sphinx was developed.
It’s a good idea to get in the habit of putting a docstring at the top of every Python file and function you write.
Running Python scripts¶
Most Python programs are written in text files ending with the .py
extension.
Some of these are simple scripts that are just a set of Python
instructions to be executed, the same things you might type at the >>>
prompt but collected in a file (which makes it much easier to modify or
reuse later). Such a script can be run at the Unix command
line simply by typing python followed by the file name.
In the above, we briefly looked at how to import a Python module from other Python codes. We will learn more in one of the following sections on how to “import” modules, and how to set the path of directories that are searched for modules when you try to import a module.
Python objects¶
Python is an object-oriented language, which just means that virtually everything you encounter in Python (variables, functions, modules, etc.) is an object of some class. There are many classes of objects built into Python and in this course we will primarily be using these pre-defined classes. For large-scale programming projects you would probably define some new classes, which is easy to do. We will take a look at some object-oriented programming with Python at the end of this chapter.
The type command can be used to reveal the type of an object:
>>> import numpy as np
>>> type(np)
<type 'module'>
>>> type(np.pi)
<type 'float'>
>>> type(np.cos)
<type 'numpy.ufunc'>
We see that np is a module, np.pi is a floating point real number, and
np.cos is of a special class that’s defined in the NumPy module.
The linspace command creates a numerical array that is also a special
NumPy class:
>>> x = np.linspace(0, 5, 6)
>>> x
array([ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5.])
>>> type(x)
<type 'numpy.ndarray'>
Objects of a particular class generally have certain operations that are
defined on them as part of the class definition. For example, NumPy
numerical arrays have a max method defined, which we can use on x in one
of two ways:
>>> np.max(x)
5.0
>>> x.max()
5.0
The first way applies the method max defined in the NumPy module
np to x.
The second way uses the fact that x, by virtue of being of type
numpy.ndarray, automatically has a max method which can be invoked (on
itself) by calling the function x.max() with no argument. Which way is
better depends in part on what you’re doing.
Here’s another example:
>>> L = [0, 1, 2]
>>> type(L)
<type 'list'>
>>> L.append(4)
>>> L
[0, 1, 2, 4]
L is a list (a standard Python class) and so has a method append that
can be used to append an item to the end of the list.
See a list of methods for Python Lists.
Declaring variables?¶
In many languages, such as Fortran, you must generally declare variables before
you can use them and once you’ve specified that, say, x is a real number.
This is the only type of things you can store in x, and a statement like
x = 'string' would not be allowed.
In Python you don’t declare variables, you can just type, for example:
>>> x = 3.4
>>> 2*x
6.7999999999999998
>>> x = 'string'
>>> 2*x
'stringstring'
>>> x = [4, 5, 6]
>>> 2*x
[4, 5, 6, 4, 5, 6]
Here x is first used for a real number, then for a character string, then
for a list. Note, by the way,
that multiplication behaves differently for objects of
different type (which has been specified as part of the definition of each
class of objects).
In Fortran if you declare x to be a real variable then it sets aside a
particular 8 bytes of memory for x, enough to hold one floating point
number. There’s no way to store 6 characters or a list of 3 integers in
these 8 bytes.
In Python it is often better to think of x as simply being a pointer
that points to some object. When you type x = 3.4 Python creates an
object of type float holding one real number and points x to that. When
you type x = 'string' it creates a new object of type str and now points x
to that, and so on.
Lists¶
We have already seen lists in the example above.
Note that indexing in Python always starts at 0:
>>> L = [4,5,6]
>>> L[0]
4
>>> L[1]
5
Elements of a list need not all have the same type. For example, here’s a list with 5 elements:
>>> L = [5, 2.3, 'abc', [4,'b'], np.cos]
Here’s a way to see what each element of the list is, and its type:
>>> for index,value in enumerate(L):
... print 'L[%s] is %16s %s' % (index,value,type(value))
...
L[0] is 5 <type 'int'>
L[1] is 2.3 <type 'float'>
L[2] is abc <type 'str'>
L[3] is [4, 'b'] <type 'list'>
L[4] is <ufunc 'cos'> <type 'numpy.ufunc'>
Note that L[3] is itself a list containing an integer and a string and
that L[4] is a function.
Here we used the function called enumerate. It returns an an
enumerated object. Several examples are:
>>> list(enumerate(L))
[(0, 5), (1, 2.3), (2, 'abc'), (3, [4, 'b']), (4, <ufunc 'cos'>)]
>>> list(enumerate(L,start=2))
[(2, 5), (3, 2.3), (4, 'abc'), (5, [4, 'b']), (6, <ufunc 'cos'>)]
In general, enumerate(thing) (or equivalently, enumerate(things,start=0) will return:
>>> (0, thing[0]), (1, thing[1]), ...
Another example is:
>>> for index in enumerate(L):
... print index
...
(0, 5)
(1, 2.3)
(2, 'abc')
(3, [4, 'b'])
(4, <ufunc 'cos'>)
Compared to this, you get:
>>> for index in enumerate(L,start=3):
... print index
...
(3, 5)
(4, 2.3)
(5, 'abc')
(6, [4, 'b'])
(7, <ufunc 'cos'>)
One nice feature of Python is that you can also index backwards from the
end: since L[0] is the first item, L[-1] is what you get going one to
the left of this, and wrapping around (periodic boundary conditions in math
terms):
>>> for index in [-1, -2, -3, -4, -5]:
... print 'L[%s] is %16s' % (index, L[index])
...
L[-1] is <ufunc 'cos'>
L[-2] is [4, 'b']
L[-3] is abc
L[-4] is 2.3
L[-5] is 5
In particular, L[-1] always refers to the last item in list L.
Copying objects¶
One implication of the fact that variables are just pointers to objects is that two names can point to the same object, which can sometimes cause confusion. Consider this example:
>>> x = [4,5,6]
>>> y = x
>>> y
[4, 5, 6]
>>> y.append(9)
>>> y
[4, 5, 6, 9]
So far nothing too surprising. We initialized y to be x and then we
appended another list element to y. But take a look at x:
>>> x
[4, 5, 6, 9]
We didn’t really append 9 to x, we appended it to the object that y
points to, which is the same object that x points to!
Failing to pay attention to this sort of thing can lead to programming nightmares.
What if we really want y to be a different object that happens to be
initialized by copying x? We can do this by:
>>> x = [4,5,6]
>>> y = list(x)
>>> y
[4, 5, 6]
>>> y.append(9)
>>> y
[4, 5, 6, 9]
>>> x
[4, 5, 6]
This is what we want. Here list(x) creates a new object, which is a list,
using the elements of the list x to initialize it, and y points to this
new object. Changing this object doesn’t change the one x pointed to.
You could also use the copy module, which works in general for any
objects:
>>> import copy
>>> y = copy.copy(x)
Sometimes it is more complicated, if the list x
itself contains other objects. See
http://docs.python.org/library/copy.html for more information.
There are some objects that cannot be changed once created (immutable
objects, as described further below).
In particular, for floats and integers, you can do things like:
>>> x = 3.4
>>> y = x
>>> y = y+1
>>> y
4.4000000000000004
>>> x
3.3999999999999999
Here changing y did not change x, luckily.
We don’t have to explicitly make a copy of x for y in this case. If we
did, writing any sort of numerical code in Python would be a nightmare.
We didn’t because the command:
>>> y = y+1
above is not changing the object that y points to, instead it is creating a new
object that y now points to, while x still points to the old object.
For more about built-in data types in Python, see http://docs.python.org/release/2.5.2/ref/types.html.
Above, we saw that append method adds a new element to the end of the existing list.
More generally, one can use insert(index, newEntry) method which will add newEntry
before index
>>> x
[4, 5, 6]
>>> x.insert(0,-10)
>>> x
[-10, 4, 5, 6]
>> x.insert(2, -20)
>>> x
[-10, 4, -20, 5, 6]
Note
Like man pages in Linux/Unix, one can invoke the built-in Python
command help to see a help page on the object under
consideration. For example, try:
>>> help(x)
and see if you can find insert, append, etc.
Note
More generally, you can also combine type and help:
>>> type(x)
<type 'list'>
>>> help(list)
or equivalently,
>>> help(x)
Likewise, you can also try help directly with specific names of
objects:
>>> help(float)
>>> help(tuple)
>>> help(dictionary)
as well as module names:
>>> import numpy as np
>>> help(np)
Don’t forget that you can always find them on more details by searching online.
In Python you can also copy multiple variables in a compact way:
>>> x=y=z=2
>>> print x, y, z
2 2 2
>>> x,y = 5.1, 159 # this is in fact a tuple assignment without using (...)
>>> x
5.1
>>> y
159
Now if you want to swap x and y, you simply do:
>>> x,y = y,x
>>> x
159
>>> y
5.1
Mutable and Immutable objects¶
Some objects can be changed after they have been created and others cannot be. Understanding the difference is key to understanding why the examples above concerning copying objects behave as they do. Here we briefly look at the following data types:
- mutable: lists (we will see dictionaries much later),
- immutable: strings, numbers, tuples.
Note
The main difference between the mutable objects and the immutable objects is the following:
id(mutable_object)doesn’t change before and after any changes inmutable_objectid(immutable_object)does change before and after any changes inimmutable_object
Lists (mutable)¶
A list is a mutable object. The statement:
$ x = [4,5,6]
above created an object that x points to, and the data held in this object
can be changed without having to create a new object. The statement:
$ y = x
points y at the same object, and since it can be changed, any change will
affect the object itself and be seen whether we access it using the pointer
x or y.
We can check this by:
>>> id(x)
1823768
>>> id(y)
1823768
The id function just returns the location in memory where the object is
stored. If you do something like x[0] = 1, you will still find that the
objects’ id’s have not changed – they both point to the same object, but the
data stored in the object has changed (Please check this out for yourself).
Strings and numbers (immutable)¶
Some data types correspond to immutable objects that, once created, cannot be changed. Integers, floats, and strings are immutable:
>>> s = "This is a string"
>>> s[0]
'T'
>>> s[0] = 'b'
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: 'str' object does not support item assignment
You can index into a string, but you can’t change a character in the string.
The only way to change s is to redefine it entirely (rather than
partially) as a new string (which will be
stored in a new object):
>>> id(s)
1850368
>>> s = "New string"
>>> id(s)
1850128
What happened to the old object? It depends on whether any other variable was pointing to it. If not, as in the example above, then Python’s garbage collection would recognize it’s no longer needed and free up the memory for other uses. But if any other variable is still pointing to it, the object will still exist, e.g.
>>> s2 = s
>>> id(s2) # same object as s above
1850128
>>> s = "Yet another string" # creates a new object
>>> id(s) # s now points to new object
1813104
>>> id(s2) # s2 still points to the old one
1850128
>>> s2
'New string'
Tuples (immutable)¶
We have seen that lists are mutable. For some purposes we need something
like a list but that is immuatable (e.g. for dictionary keys, see below). A
tuple is like a list and it is immutable. It is defined with
parentheses (..) (you can define a tuple without parentheses in principle)
rather than square
brackets [..] as used in lists:
>>> t = (4,5,6) #this is same as t = 4,5,6
>>> t[0]
4
>>> t[0] = 9
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
Iterators¶
We often want to iterate over a set of things. In Python there are many ways to do this, and it often takes the form:
>>> for A in B:
... # do something, probably involving the current A
In this construct B is any Python object that is iterable, meaning it
has a built-in way (when B’s class was defined) of starting with one thing
in B and progressing through the contents of B in some hopefully logical
order.
Lists and tuples are iterable in the obvious way: we step through it one element at a time starting at the beginning:
>>> for i in [3, 7, 'b']:
... print "i is now ", i
...
i is now 3
i is now 7
i is now b
range¶
In numerical work we often want to have i start at 0 and go up to some number N, stepping by one. We obviously don’t want to have to construct the list [0, 1, 2, 3, ..., N] by typing all the numbers when N is large, so Python has a way of doing this:
>>> range(7)
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
Note that the last element is 6, not 7. The list has 7 elements but starts by default at 0, just as Python indexing does. This makes it convenient for doing things like:
>>> L = ['a', 8, 12]
>>> for i in range(len(L)):
... print "i = ", i, " L[i] = ", L[i]
...
i = 0 L[i] = a
i = 1 L[i] = 8
i = 2 L[i] = 12
Note that len(L) returns the length of the list, so range(len(L)) is
always a list of all the valid indices for the list L.
enumerate¶
Another way to do this is:
>>> for i,value in enumerate(L):
... print "i = ",i, " L[i] = ",value
...
i = 0 L[i] = a
i = 1 L[i] = 8
i = 2 L[i] = 12
range can be used with more arguments, for example if
you want to start at 2 and step by 3 up to 20:
>>> range(2,20,3)
[2, 5, 8, 11, 14, 17]
Note that this doesn’t go up to 20. Just like range(7) stops at 6, this
list stops one item short of what you might expect.
NumPy has a linspace command that behaves like Matlab’s, which is
sometimes more useful in numerical work, e.g.:
>>> np.linspace(2,20,7)
array([ 2., 5., 8., 11., 14., 17., 20.])
This returns a NumPy array with 7 equally spaced points between 2 and 20, including the endpoints. Note that the elements are floats, not integers. You could use this as an iterator too.
If you plan to iterate over a lot of values, say 1 million, it may
be inefficient to generate a list object with 1 million elements using
range. So there is another option called xrange, that does the
iteration you want without explicitly creating and storing the list:
for i in xrange(1000000):
# do something
does what we want.
Note that the elements in a list you’re iterating on need not be numbers.
For example, the sample module myfcns.py in
/lectureNote/chapters/chapt03/codes/examples
defines two functions f1 and f2:
If we want to evaluate each of them at x=3., we could do:
>>> from myfcns import f1, f2
>>> type(f1)
<type 'function'>
>>> for f in [f1, f2]:
... print f(3.)
... print f()
...
5.0
2.0
9.0
0.0
This can be very handy if you want to perform some tests for a set of test
functions. Notice that the arguement x=0. of the two functions
in myfcns.py is used by default when there is no argument is
passed in.
